Review this previous post http://hodentekmsss.blogspot.com/2014/11/accessing--
sql-server-via-smo-using.html
In the above post you will get an introduction to Power Shell and SQL Server
Management Objects. You also learn how to access the SQL Server and carry out a
few tasks like listing out all the databases.
Review this post for creating a database using Power Shell and SQL Server
Management Objects:
http://hodentekmsss.blogspot.com/2015/02/creating-database-using-power-shell-
and.html
In the above post you will learn how to create a new database in SQL Server using
SMO and Power Shell. Using Transact-SQL or the SSMS you can easily create a
database. Using PowerShell is another option to create a database using a script.
Having created a database you would want to create tables in the database.
This post shows how you may create a table. This script has been tested to work with
Power Shell ver. 4.0.
Launch SQLPS from Start | Run and type-in SQLPS and click OK.
PS_SMOTable01.png
Let us get connected to the instance of SQL Server (RegencyPark) on this computer
(Hodentek8) by (declaring) running the command shown.
PS SQLSERVER:\> $server= new-object Microsoft.Sqlserver.management.smo.server
'Hodentek8\RegencyPark'
Let us create a database named 'Feb6'.
Declare a name for the database as shown here:
PS SQLSERVER:\SQL\HODENTEK8\REGENCYPARK> $dbname= "Feb6"
Now create a database object variable in the instance using SMO:
PS SQLSERVER:\> $db=new-object Microsoft.Sqlserver.management.smo.Database
($server,$dbname)
Now create the database using the create () function.
PS SQLSERVER:\> $db.Create()
When you run the above command you will have created a database called Feb6 in the
SQL Server instance as shown (this may take a few seconds and you will not get any response except if there are errors) in SQL Server Management Studio:
PS_SMOTable02.png
In creating the table run the following lines of command in PS SQLSERVER:\>:
We declare a name for the table as 'SmoCustomers' and instantiate the table object
by running the following:
$tbname = "SmoCustomers"
$tb = new-object Microsoft.Sqlserver.management.smo.Table ($db, $tbname)
We assume the table to have three columns (fields) named 'Field1, Field2 and
Field3. Field1 is of int data type and the two others are nvarchar(num) data type.
Typically instantiate a column object and its data type and add that column to the
$tb.Columns. Carry out this for the three columns by running these lines in PS
SQLSERVER:\>.
$colField1 = New-Object Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Column ($tb, "Field1")
$colField1.DataType = [Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Datatype]::Int
$tb.Columns.Add($colField1)
$colField2 = New-Object Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Column ($tb, "Field2")
$colField2.DataType = [Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Datatype]::NVarchar(25)
$tb.Columns.Add($colField2)
$colField3 = New-Object Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Column ($tb, "Field3")
$colField3.DataType = [Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Datatype]::NVarchar(25)
$tb.Columns.Add($colField3)
Now create the table by running the following code:
$tb.create ()
Here is the complete line-by-line code:
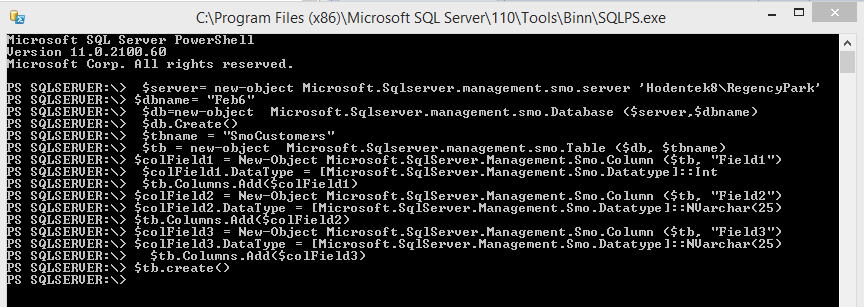
PS_SMOTable03.png
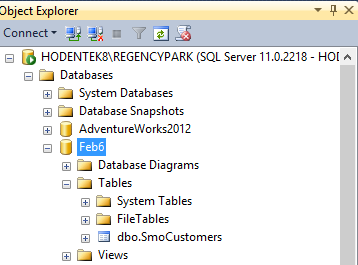
Again do not look out for a response but check for the table in Feb6 database you
created earlier.
PS_SMOTable04.png
sql-server-via-smo-using.html
In the above post you will get an introduction to Power Shell and SQL Server
Management Objects. You also learn how to access the SQL Server and carry out a
few tasks like listing out all the databases.
Review this post for creating a database using Power Shell and SQL Server
Management Objects:
http://hodentekmsss.blogspot.com/2015/02/creating-database-using-power-shell-
and.html
In the above post you will learn how to create a new database in SQL Server using
SMO and Power Shell. Using Transact-SQL or the SSMS you can easily create a
database. Using PowerShell is another option to create a database using a script.
Having created a database you would want to create tables in the database.
This post shows how you may create a table. This script has been tested to work with
Power Shell ver. 4.0.
Launch SQLPS from Start | Run and type-in SQLPS and click OK.
PS_SMOTable01.png
Let us get connected to the instance of SQL Server (RegencyPark) on this computer
(Hodentek8) by (declaring) running the command shown.
PS SQLSERVER:\> $server= new-object Microsoft.Sqlserver.management.smo.server
'Hodentek8\RegencyPark'
Let us create a database named 'Feb6'.
Declare a name for the database as shown here:
PS SQLSERVER:\SQL\HODENTEK8\REGENCYPARK> $dbname= "Feb6"
Now create a database object variable in the instance using SMO:
PS SQLSERVER:\> $db=new-object Microsoft.Sqlserver.management.smo.Database
($server,$dbname)
Now create the database using the create () function.
PS SQLSERVER:\> $db.Create()
When you run the above command you will have created a database called Feb6 in the
SQL Server instance as shown (this may take a few seconds and you will not get any response except if there are errors) in SQL Server Management Studio:
PS_SMOTable02.png
In creating the table run the following lines of command in PS SQLSERVER:\>:
We declare a name for the table as 'SmoCustomers' and instantiate the table object
by running the following:
$tbname = "SmoCustomers"
$tb = new-object Microsoft.Sqlserver.management.smo.Table ($db, $tbname)
We assume the table to have three columns (fields) named 'Field1, Field2 and
Field3. Field1 is of int data type and the two others are nvarchar(num) data type.
Typically instantiate a column object and its data type and add that column to the
$tb.Columns. Carry out this for the three columns by running these lines in PS
SQLSERVER:\>.
$colField1 = New-Object Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Column ($tb, "Field1")
$colField1.DataType = [Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Datatype]::Int
$tb.Columns.Add($colField1)
$colField2 = New-Object Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Column ($tb, "Field2")
$colField2.DataType = [Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Datatype]::NVarchar(25)
$tb.Columns.Add($colField2)
$colField3 = New-Object Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Column ($tb, "Field3")
$colField3.DataType = [Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Datatype]::NVarchar(25)
$tb.Columns.Add($colField3)
Now create the table by running the following code:
$tb.create ()
Here is the complete line-by-line code:

PS_SMOTable03.png
Again do not look out for a response but check for the table in Feb6 database you
created earlier.
PS_SMOTable04.png





No comments:
Post a Comment